
L-Glutathione Reduced
Reduced glutathione is a natural tripeptide composed of glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine. Present in human cells, it plays a crucial role in metabolic regulation. Known for its ability to activate multiple enzymes, reduced glutathione promotes the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Its detoxification, antioxidant, and immune-enhancing effects are widely recognized and utilized in various healthcare products.
CAS : 70-18-8
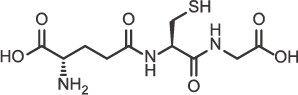
Molecular Weight : 307.3
Molecular Formula : C10H17N3O6S
HPLC Purity : ≥98%


Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can induce tissue fibrosis by accelerating the abnormal proliferation of malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE). Reduced glutathione (GSH) mitigates tissue fibrosis by eliminating ROS. Additionally, ROS disrupt lipid homeostasis, inhibit fatty acid oxidation, and cause lipid peroxidation. GSH prevents lipid peroxidation by neutralizing ROS.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can stimulate the production of inflammatory factors, leading to inflammation. Reduced glutathione (GSH) exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by neutralizing ROS. Additionally, ROS can activate tyrosinase, leading to increased melanin production and skin hyperpigmentation. GSH can brighten the skin by mitigating ROS.

Fifteen patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease were supplemented with 300 mg/day of glutathione for four months. After the treatment period, a significant decrease in plasma alanine transaminase (ALT) levels was observed.

Fifteen HIV-positive patients were randomly assigned to two groups. One group received a glutathione supplement (1260 mg/day). After 13 weeks, this group exhibited a significant decrease in the inflammatory marker IL-6.

Sixty healthy individuals were administered 500 mg/day of glutathione orally. After four weeks, the average melanin index across six areas showed a significant decrease compared to the control group.